- Published on
This Week I learned 6
Summary
1. [Dev] NextJS Page Router vs App Router
2. [Paper] AffordGrasp - In-Context Affordance Reasoning for Open-Vocabulary Task-Oriented Grasping in Clutter
3. [Paper] 3D-AFFORDANCELLM: HARNESSING LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS FOR OPEN-VOCABULARY AFFORDANCE DETECTION IN 3D WORLDS
4. [Paper] LASO: Language-guided Affordance Segmentation on 3D Object
5. [Paper] Open-Vocabulary Affordance Detection in 3D Point Clouds
6. [Paper] GREAT: Geometry-Intention Collaborative Inference for Open-Vocabulary 3D Object Affordance Grounding
[Dev] NextJS Page Router vs App Router
Page Router
- Nextjs 의 전통적인 라우팅 방식
/pages디렉토리 내에서 정의, 파일명이 경로의 페이지가 됨- 파일 시스템을 기반으로 라우팅이 이뤄짐
pages/
├── index.js // '/' 경로
├── about.js // '/about' 경로
├── blog/
├── index.js // '/blog' 경로
└── [slug].js // '/blog/post-name' 경로
App Router
- Nextjs 13 에서 도입된 새로운 라우팅 방식
/app디렉토리 내에서 정의,page.js파일이 경로의 페이지가 됨- Page Router 와 다른 점
- React Server Components 지원
- Page Router 는 hybrid 방식, 즉 서버에서 먼저 실행하고, 상호작용을 위해 클라이언트에서도 실행되어야 함 → 모든 코드가 client 로 전송
- App Router 에서는 server component, client component 를 지정할 수 있음 →
”use client”가 필요한 이유 - 컴포넌트에서 직접 데이터 패칭이 가능함, server component 코드는 client 에 전송되지 않음
- 디렉토리 별 레이아웃 설정 - 디렉토리 별로
layout.js를 만들 수 있음 Streaming과<Suspense>지원- 컴포넌트 내에서 보다 쉽게 데이터 패칭 가능(특별한 함수 필요 없음, async/await 로 가능)
- React Server Components 지원
app/
├── page.js // '/' 경로
├── layout.js // 루트 레이아웃
├── about/
│ └── page.js // '/about' 경로
├── blog/
│ ├── page.js // '/blog' 경로
│ ├── layout.js // 블로그 섹션 레이아웃
│ └── [slug]/
│ └── page.js // '/blog/post-name' 경로
└── api/
└── users/
└── route.js // API 라우트
Nextjs streaming and Suspense
Nextjs 18 부터 App Router 를 통해 지원
Streaming
- 페이지의 모든 내용이 준비될 때까지 기다리지 않고, 준비된 부분부터 순차적으로 클라이언트에 전송
// 전통적인 방식: 모든 데이터가 준비될 때까지 대기 async function Page() { const userData = await fetchUser(); // 2초 const postsData = await fetchPosts(); // 3초 // 총 5초 후에 페이지 전체가 한번에 표시됨 return ( <div> <UserProfile user={userData} /> <PostsList posts={postsData} /> </div> ); } // 스트리밍 방식: 준비된 부분부터 점진적으로 표시 function Page() { return ( <div> <Suspense fallback={<UserSkeleton />}> <UserProfile /> {/* 2초 후 표시 */} </Suspense> <Suspense fallback={<PostsSkeleton />}> <PostsList /> {/* 3초 후 표시 */} </Suspense> </div> ); }Suspense
- 비동기 작업 완료시까지 대체 UI 를 보여주는 React 의 기능
// app/dashboard/page.js import { Suspense } from 'react'; export default function Dashboard() { return ( <div> <h1>대시보드</h1> {/* 사용자 정보 영역 */} <Suspense fallback={<div>사용자 정보 로딩중...</div>}> <UserInfo /> </Suspense> {/* 차트 영역 */} <Suspense fallback={<ChartSkeleton />}> <Analytics /> </Suspense> {/* 최근 활동 영역 */} <Suspense fallback={<div>활동 내역 불러오는 중...</div>}> <RecentActivity /> </Suspense> </div> ); } // 각 컴포넌트는 독립적으로 데이터를 페칭 async function UserInfo() { const user = await fetch('/api/user').then(res => res.json()); return <div>안녕하세요, {user.name}님!</div>; } async function Analytics() { const data = await fetch('/api/analytics').then(res => res.json()); return <Chart data={data} />; }
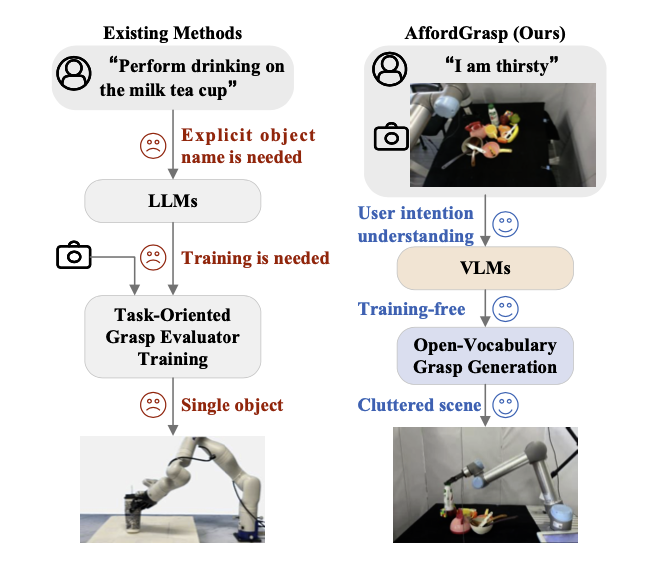
[Paper] AffordGrasp - In-Context Affordance Reasoning for Open-Vocabulary Task-Oriented Grasping in Clutter
Task
- task-oriented grasping based on affordances
- affordance 를 고려하여 테스크에 맞게 대상 객체를 grasping 하는 것을 목표로 함
- Annotated dataset: task-oriented method 들은 많은 training data 를 요구하며, 특정 테스크에 대해서만 다루는 데이터로 인해 일반화가 어렵다는 문제가 있음. Open Vocabulary 에 적용하기 어려움
- Ambiguity in user instructions: explicit 하게 프롬프트를 작성해주어야 하는 연구가 많음. “I am thirsty” 와 같은 추상적이고 함축적인 명령에 대한 연구가 부족함
- Cluttered scenes: 다양한 객체가 함께 등장할 때 대상 객체를 식별하고 Task 에 맞게 적절히 grasp 하는 연구가 없음
- Arm: Gripper
- Input: RGB-D + 사용자의 instruction
- Model: GPT-4o(VLM), Part Segmentation(VLPart), AnyGrasp
AffordGrasp
- 세 가지 단계로 구성
- In-Context Affordance Reasoning
- Visual Affordance Grounding
- Grasp Pose Generation
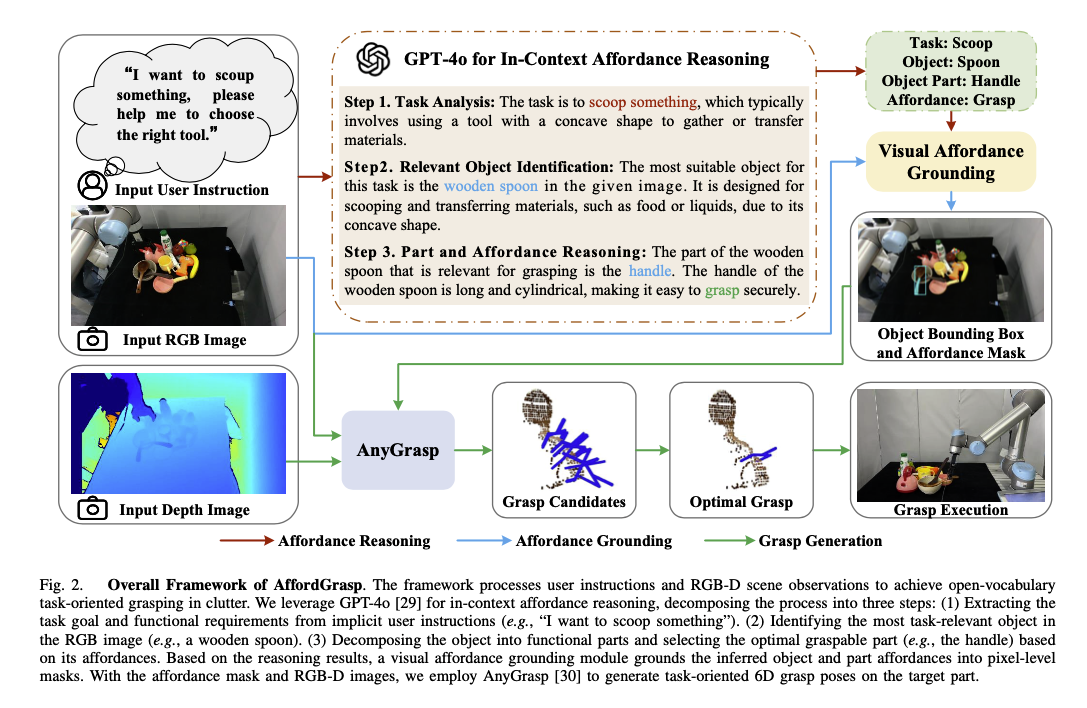
In-Context Affordance Reasoning
- Task Analysis
- 사용자의 Instruction 과 RGB Image 를 입력으로 받아 GPT-4o 를 통해 explicit 한 Task 를 추출
- Relevant Object Identification
- 추출된 Task 에 따라 이미지 상에서 가장 관련 있는 객체 특정
- Part and Affordance Reasoning
- 선택된 객체를 여러 개의 기능적 영역과 그에 맞는 affordance 로 쪼갬
- 그 중 최적의 영역과 affordance 를 선택함
- 이를 통해 복잡한 시나리오도 해결 가능하고, 설명 가능성도 높힘
- 추론의 결과물은 task, object, object part, affordance 가 됨 → 다음 모듈의 입력
Visual Affordance Grounding
- RGB 이미지와 part, affordance 를 입력으로 받아, object bbox 와 affordance mask 를 생성하는 단계
- VLPart 사용 - Open-Vocabulary Part Segmentation Method
- Object Localization
- VLPart 를 사용하여 객체에 대한 bbox 와 masked image 를 생성함
- Affordance Mask Prediction
- Object Localization 의 Mask image 와 part, affordance 를 VLPart 의 입력으로 주어, affordance mask 를 생성함
Grasp Pose Generation
- Visual affordance 를 입력으로 AnyGrasp 를 활용해 6D grasp posed 를 생성함
- Depth 이미지를 partial-view point cloud 로 변환함(using camera intrisics)
- affordance mask 로 point coud 를 필터링함
- affordance 에 맞는 point cloud 생성을 목적으로 함
- 이를 통해 grasp 생성 과정을 제약하고, 주변 객체로부터 간섭을 방지함(못 잡는 영역을 제거하는 것)
- object의 잡을 수 있는 영역을 나타내는 point cloud 를 AnyGrasp 에 입력으로 전달하여 grasp candidate 생성
- AnyGrasp
- 이미지를 입력으로 받아 Gripper 로 집어낼 수 있는 모델
- Depth Camera 를 통해 single-view point cloud 를 주된 입력으로 하여 객체를 집어냄
- AnyGrasp 의 candidate 구조
- grasp pose:
- rotation matrix:
- translation vector:
- minimum gripper width:
- optimal grasp pose:
- confidence score:
- translation vector:
- affordance mask centroid:
- translation vector 가 affordance mask centroid 에 가까울수록, confidence score 가 높을수록 optimal
Experiment Setup
- Hardware RTX 4090 24GB x 1
- Simulation
- env: PyBullet
- arm: UR5 arm with ROBOTIQ-85 gripper
- camera: RealSense L515
- Image size: 224x224
- grasp pose generation: GraspNet
- Real-World
- arm: UR5 arm with RS-485
- camera: RealSense L515
- Image size(RGB-D): 1280 x 720
- grasp pose generation: AnyGrasp
- Baseline Methods: RAM, AnyGrasp, ThinkGrasp
- Evaluation Metric: Grasp Success Rate(GSR)
Simulation result
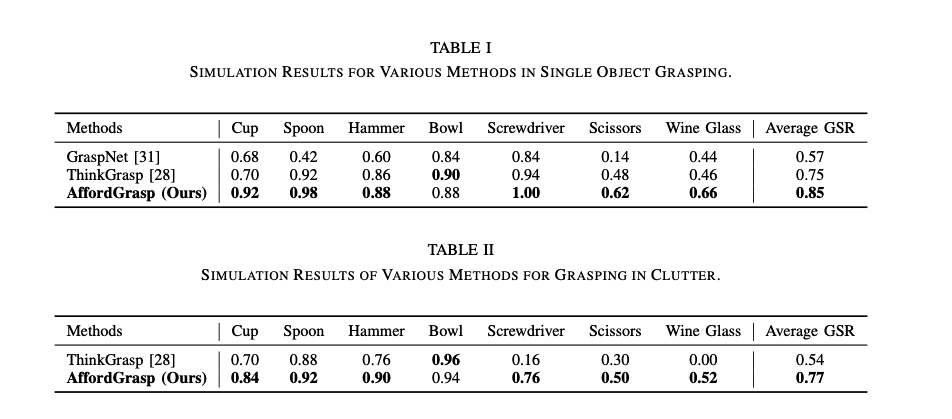
- Grasping single Object
- GraspNet, ThinkGrasp 와 비교해 볼 때 가장 성능이 좋음
- Grasping in Clutter
- 다른 객체들이 타겟 객체와 함께 임의로 생성되는 상황
- ThinGrasp 보다 성능이 좋음
RealWorld Result
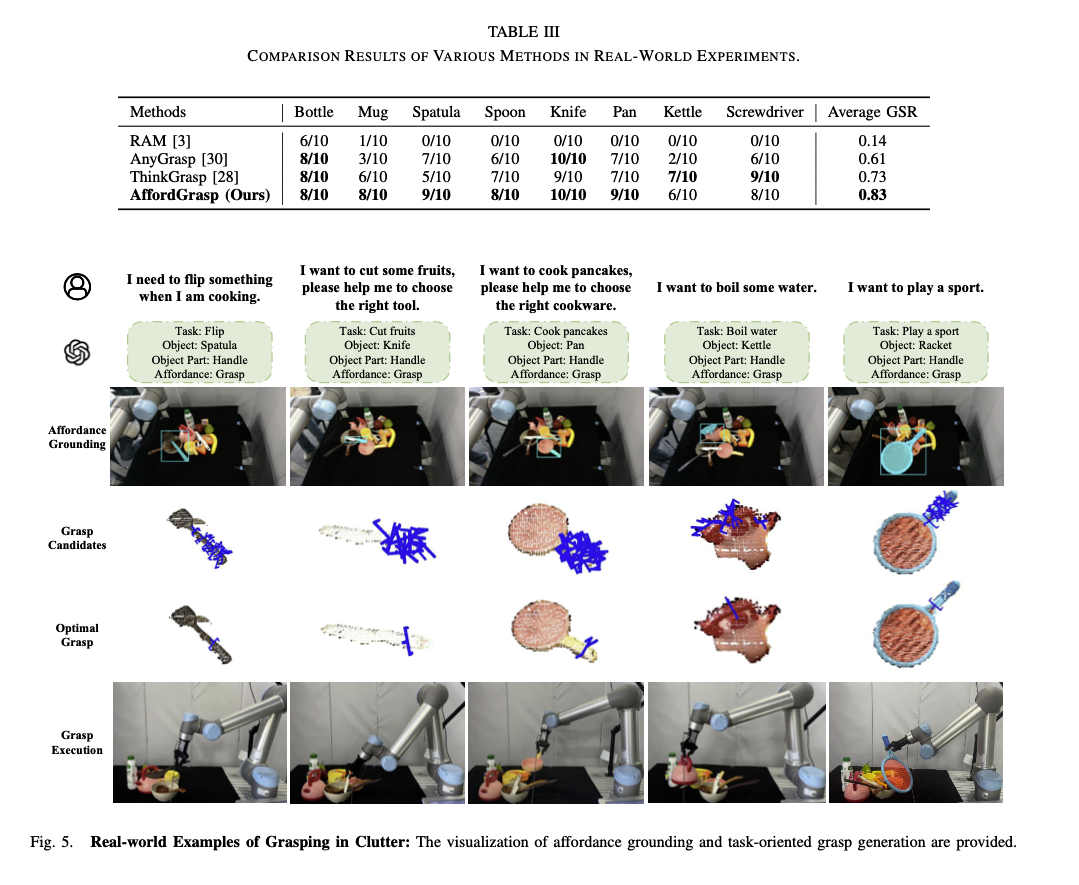
- RAM, GraspNet, ThinkGrasp 와 비교해 볼 때 가장 성능이 좋음
[Paper] 3D-AFFORDANCELLM: HARNESSING LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS FOR OPEN-VOCABULARY AFFORDANCE DETECTION IN 3D WORLDS
Reformulation of Affordance Detection
- Affordance detection 문제는 “상호작용하기에 가장 적합한 객체의 영역을 특정”하는 문제임
- 기존 방법의 한계 → open-world scene 에 대한 제한적인 일반화 성능
- 사전에 정의된 레이블 데이터를 필요로 함, 복잡한 자연어를 처리하는 데에 어려움이 있음
- 이를 극복하기 위해 Instruction Reasoning Affordance Segmentation(IRAS) task 로 문제를 재정의함
- language context 와 object affordance 간의 연결을 강화하는 것을 목표
- instruction 과 object point cloud 입력 → affordance region 을 나타내는 binary mask 반환
3D-AffordanceLLM
- LLM 을 활용함
- LLM 은 world knowledge 를 가지고 있으며, 추론 능력고 갖추고 있음
- mug 를 안전히 드는 방법에 대해 물어보면 LLM 은 손잡이 부분을 집어야 한다는 것을 알고 있음
- 이를 활용하면 unseen context 에서도 잘할 것
- 두 개의 main component
- Point Cloud Multimodal Model: Point Cloud 와 사용자의 instruction 을 받아
Special Token <AFF>를 포함하는 response 생성 - Affordance Decoder(AFD): point cloud 와
<AFF>토큰을 통해 segmentation point feature 를 생성
- Point Cloud Multimodal Model: Point Cloud 와 사용자의 instruction 을 받아
- 3D-LLM 관련 연구들은 있었음
- 한계: 텍스트, bbox 를 출력함, 하지만 segmentation mask 를 출력하지는 않음
- Lisa 에서는 2D 도메인에서 segmentation mask 를 출력함. 여기서 영감.
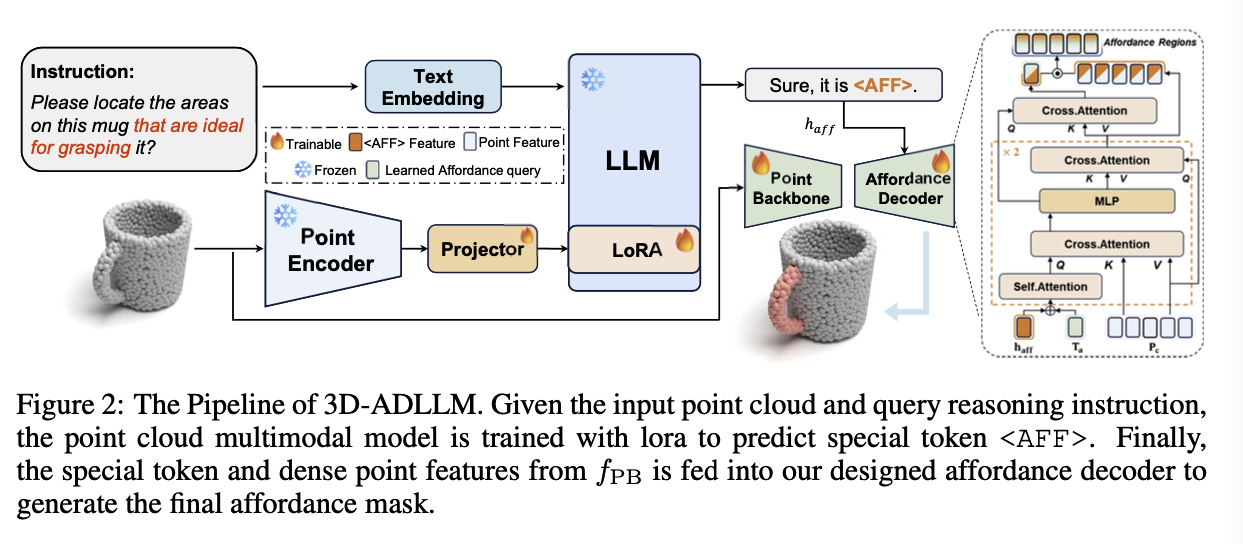
Model Architecture
- Point Encoder / Point backbone
- 3d point cloud 를 sequence 로 만드는 과정
- input: Point Cloud
- : number of points, : dim of each point
- output: 일련의 points
- : number of points, : feature dim
- LLM Projector
- point token 으로 만들어 LLM 의 입력으로 넣을 수 있게 만드는 과정
- input: 일련의 points
- output: point token
- Language Model
- input: text token 과 3d point cloud tokens -
- output: output tokens -
- Affordance Decoder
- query based method 적용
- LLM 이 이해한 instruction 과 3D point cloud 정보를 연결해 Affordance Mask 를 통합하여 출력
<AFF>토큰- LLM 이 추출한 정보를 잘 다루기 위해 추가한 special token
- LLM 의 출력은 다음과 같은 형태로 이뤄짐 = “Sure, it is
<AFF>.” - 이때 affordance mask 를 만드는 데에 필요한 정보는
<AFF>에 들어 있음. <AFF>토큰() 을 MLP 레이어에 통과시켜 얻은 를 decoder 에 전달함
Multi-Stage Training
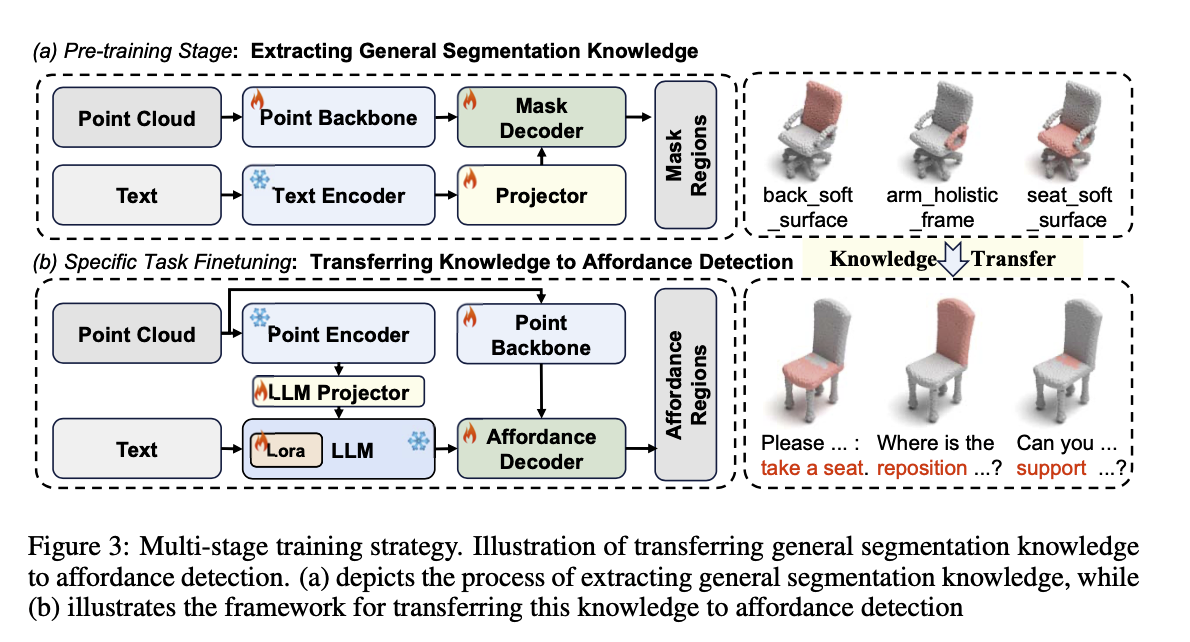
- 데이터셋이 부족하여 multi-stage 로 학습을 진행함
- stage 1: 일반적인 segmentation task
- stage 2: affordance detection
Experiments
- Model Architecture
- LLM: Phi-3.5-mini-instruct
- point encoder: Point-BERT, pretrained with ULIP-2 + ModelNet Dataset
- backbone: Point Trainformer
- Baseline Models: ZSLPC, TZSLPC, 3DGenZ, OpenAD, IAGNet, LASO, ShapeLLM
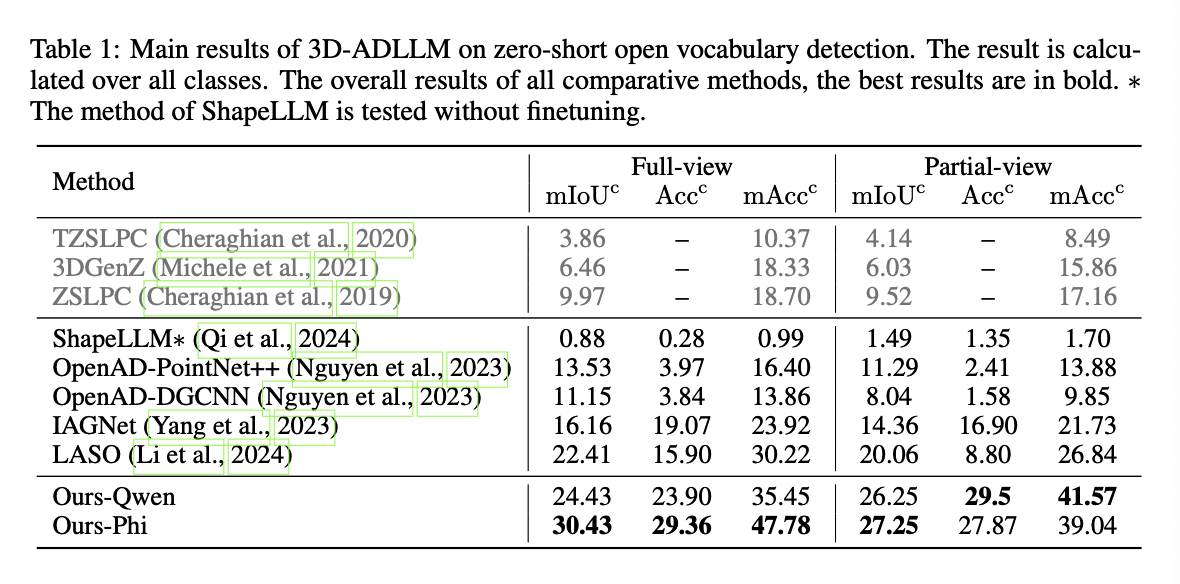
- Metrics
- mIoUc(mean IoU over all classes): 각 어포던스 유형(class)에 대한 IoU의 평균
- Accc(overall accuracy over all points): 모든 포인트에 대한 정확도
- mAccc(mean accuracy over all classes): 클래스별 평균 정확도 - 클래스별 불균형을 고려한 지표
- 모든 metric 에 대한 계산은 point 를 단위로 이뤄짐
[Paper] LASO: Language-guided Affordance Segmentation on 3D Object
Concept
- 3D 데이터에서 의미를 고려한 affordance segmentation 연구가 부족함
- LASO 는 주어진 언어 지시(affordance question)와 관련된 부분을 segment 하는 “테스크” 를 말함
- contribution
- LASO Task 에 맞는 데이터셋 제안
- PointRefer 모델 제안 - Adaptive Fusion Module, linguistic cues to generate dynamic kernel
Method Overview: PointRefer
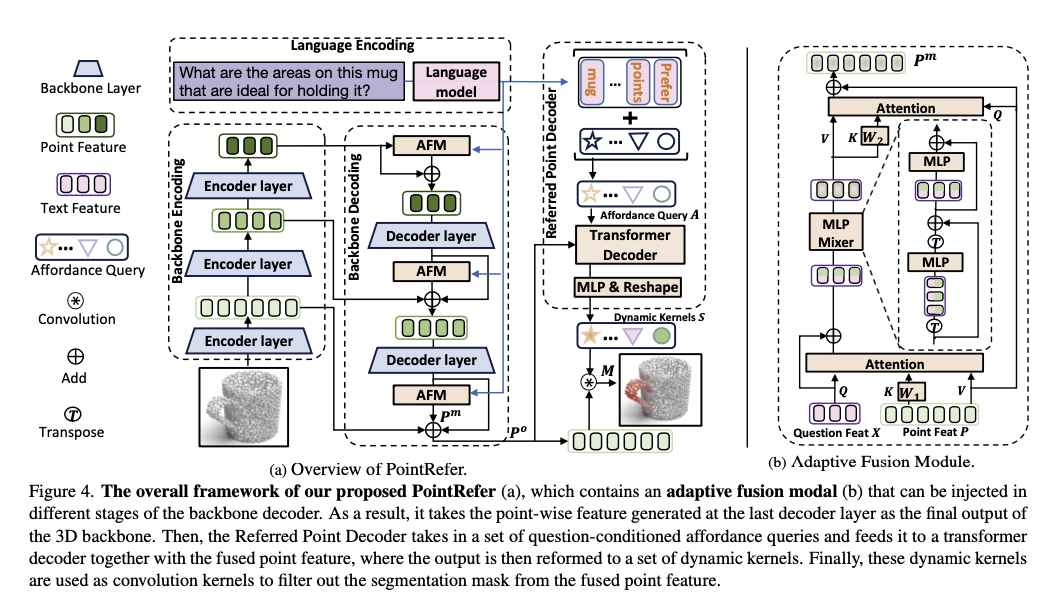
- affordance 의 다양한 스케일을 가정함
- 핵심 구성 요소: 3D backbone, Adaptive Fusion Module(AFM), Referred Point Decoder(RPD)
- 3D backone
- point cloud 를 입력으로 받아 처리, encoder-decoder 구조
- Adaptive Fusion Module(AFM)
- backbone 의 decoding stage 에서 text clue 를 주입하는 방법
- multi-scale cross-modal fusion
- Referred Point Decoder(RPD)
- segmentation mask 를 예측하는 부분
- affordance query 를 transformer decoder 의 입력으로 함
- 질문에서 참조된 포인트들만 집중적으로 분석하도록 학습 → 질문의 의미를 인지하는 dynamic kernel 생성
- dynamic kernel 을 convolute 하여 최종 분할 마스크 추출
[Paper] Open-Vocabulary Affordance Detection in 3D Point Clouds
Concept
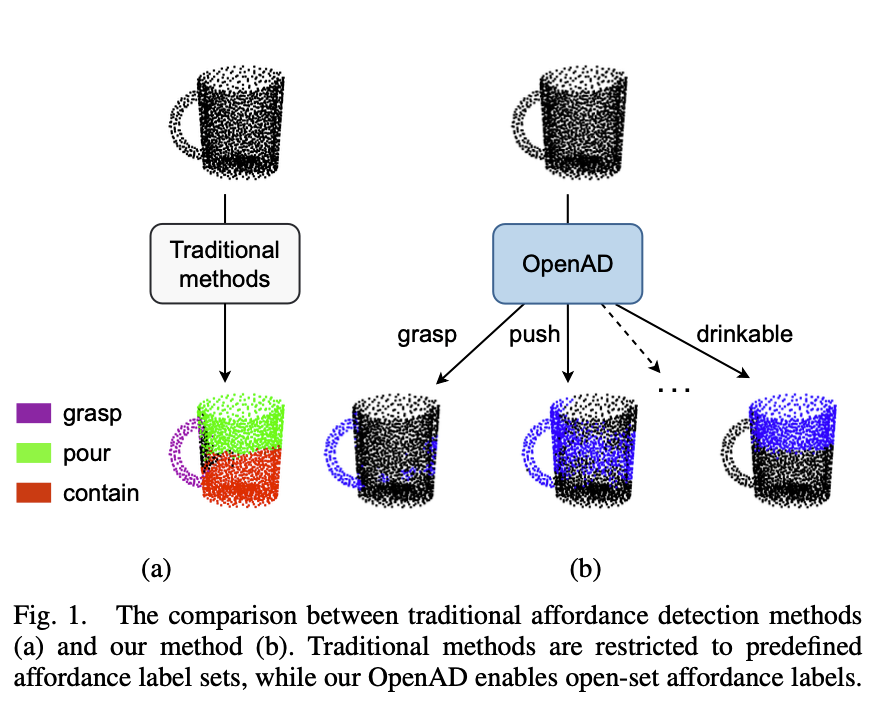
- Affordance detection 문제를 다룸
- 기존 방법들은 predefined set of affordance labels 를 다룸 → 복잡하고 동적인 환경에서는 적용이 어려움
- OpenAD(Open-Vocabulary Affordance Detection)
- 논문에서 제안하는 방법
- 3D point cloud 에서 affordance 를 찾아냄
- zero-shot detection, unseen affordances 에 대해서도 잘 동작함
Method Overview
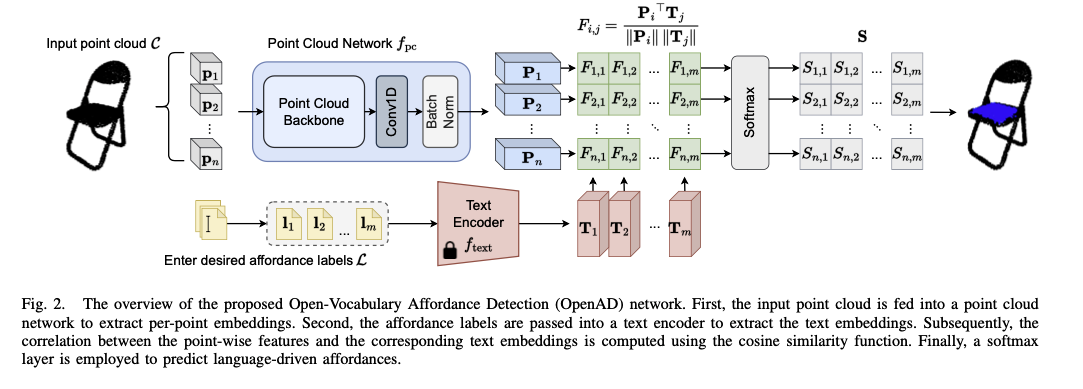
- Architecture
- Point Cloud Network 로 input point cloud 에서 Feature 를 추출함
- 자연어로 된 Label 은 Text Encoder 로 encoding 함
- Point cloud feature 와 text encoding 간의 similarity 를 계산, 이 때 label 과 관련있는 point 들이 masking 될 수 있도록 학습 진행
- Text Encoder
- LLM 을 사용하지 않음
- CLIP’s ViT-B/32 을 사용함. 학습을 따로 진행하지 않음
- Point Cloud Network
- PointNet++ 를 사용함.
- Backbone 뒤에 1D Conv layer 를 추가함 → point cloud feature 의 크기를 맞추는 역할
- Learning text-point correlation
- correlation:
- softmax with learnable param :
- Matrix 는 X 로, 각 Point 가 어떤 Class 로 분류될지 나타냄
[Paper] GREAT: Geometry-Intention Collaborative Inference for Open-Vocabulary 3D Object Affordance Grounding
Concept
- 3D object 에서 action possibilities region 을 찾는 것이 3D object affordance grounding task 의 주요 목적 중 하나
- 기존 방법은 동일한 어포던스를 가진 객체들 간에 내재된 불변 기하학적 구조(implied invariant geometries)와 잠재적 상호작용 의도(potential interaction intentions)를 활용하지 못함 → 제한된 의미론적 공간에 취약함
- 사람은 multi-step reasoning 으로 복잡한 문제를 해결하고, 연상과 유추를 통해 다양한 상황에 대응함
- GREAT 프레임워크 제안
- Open-Vocabulary 3D Object Affordance Grounding 을 목적으로 함
- 불변의 기하학적 구조 발굴 + 시나리오 유추/추론 → affordance knowledge 형성
- affordance knowledge 와 기하학적 구조 및 시각적 정보와 결합하여 3D Object Affordance 를 grounding 함
Method Overview
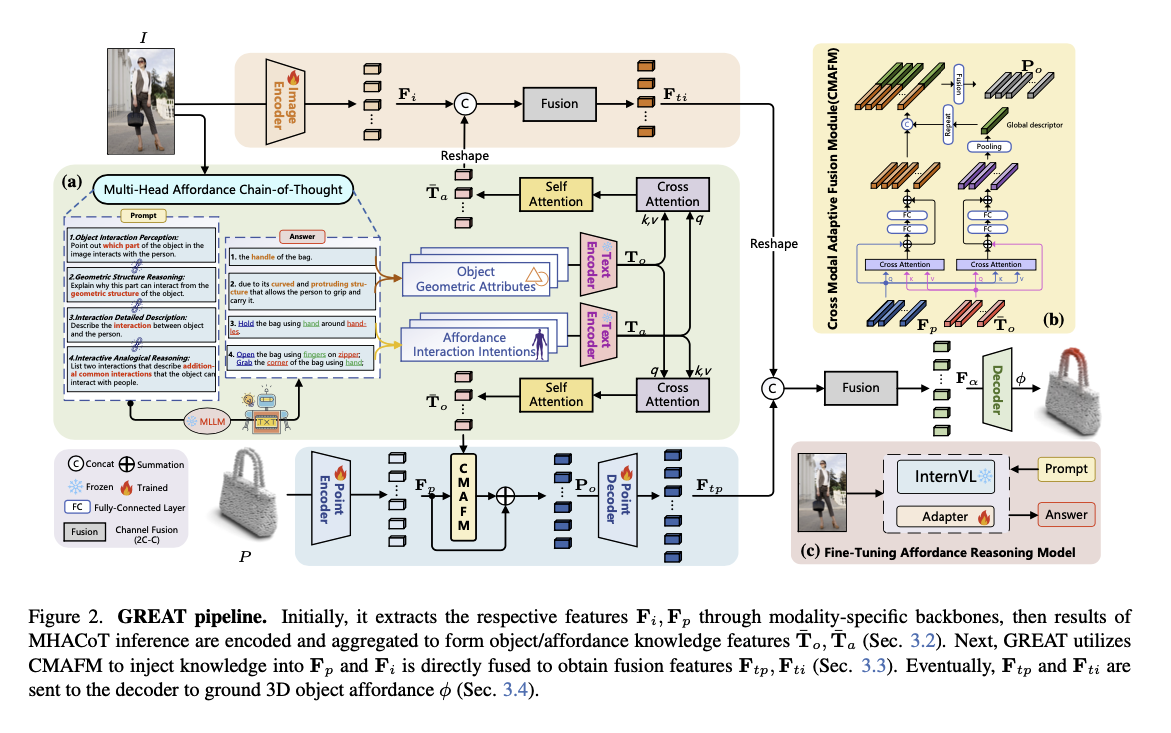
- 입력으로 Point Cloud(Nx3) 와 Image(3xHxW) 를 받음
- 각각 PointNet++ 와 ResNet 에 통과시켜, 와 를 얻음
- Multi-Head Affordance CoT(MHACoT) 를 활용해 “Object Geobetric Attributes”와 “Affordance Interaction Intentions”를 추론함
- 두 가지를 Text Encoder Roberta 로 인코딩 + Cross Attention 적용하여 다음 두 가지 추출
- : 객체 기하학적 특징 (Object Geometric Feature).
- : 어포던스 의도 특징 (Affordance Intention Feature)
- Cross-Modal Adaptive Fusion Module(CMAFM) 을 통해 Point Cloud 정보와 MHACoT 로 부터 추출한 정보를 통합함.
- 디코딩하여 최종 3D Affordance 를 출력함.
[Paper] Grounding 3D Object Affordance with Language Instructions, Visual Observations and Interactions
Concept

- Grounding 3D object affordance 는 객체의 조작 가능한 3D 공간을 찾는 테스크임
- Language Instruction, Visual Observation, Interaction 을 기반으로 이를 수행하는 새로운 프레임워크 - LMAAffordance3D 제안
- 최초의 멀티 모달, language-guided grounding network
- VLM 을 사용하여 2D, 3D 공간의 특징을 의미론적 특징과 융합함
Method Overview
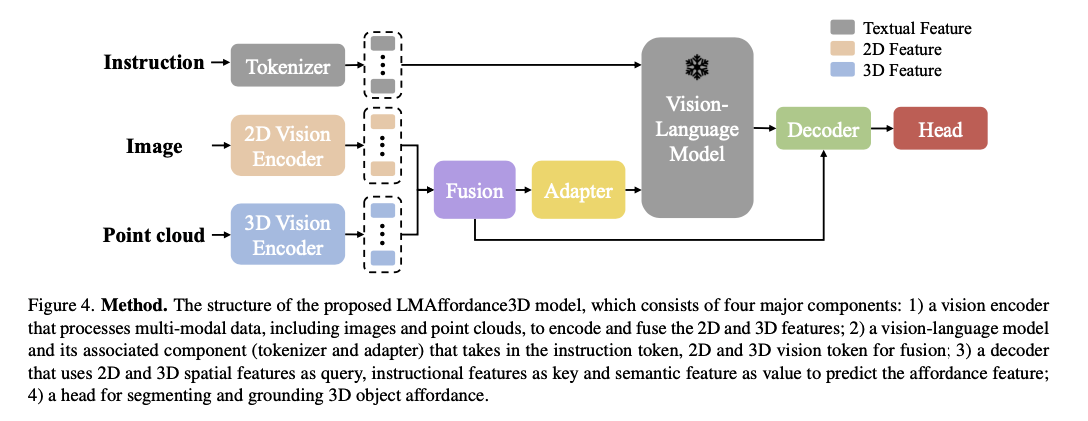
- 입력으로 Instruction(text), Image(2D), Point Cloud(3D) 를 받음
- Vision Encoder + Fusion - 2D와 3D는 가지고 있는 정보가 서로 다름. 2D 이미지에서는 객체의 색깔이나 객체 간의 상호 작용 정보를, 3D Point Cloud 에서는 객체의 크기와 형태를 추출할 수 있음
- Multi-Modal Vision Encoder
- 2D: ResNet18
- 3D: PointNet++
- Fusion: MLP + Self-Attention
- Multi-Modal Vision Encoder
- VLM 으로 Instruction 정보와 2D 3D Fusion 정보를 처리함
- LLaVA-7B
- Adapter = MLP = 2 linear layer + 1 act function
- Decoder 에서는 Fusion정보를 query로, instruction feature 를 key 로, 의미론적 특징을 value 로 하여 어포던스 특징을 예측함
- VLM 의 아웃풋은 instruction feature 와 semantic feature 로 분할하여 사용
- Fusion 에서 가져온 정보를 Spatial feature 로 사용
- 이들을 활용해 Cross Attention 을 적용함
- Head 에서는 3D Object Affordance 를 Segment 함
- Upsampling 을 수행하여 point cloud 의 포인트 갯수를 복원함
- BatchNorm 이 추가된 MLP